Bone pain is usually the earliest symptom suggestive that cancer has disseminated to the bones. At first, the pain may be constant or intermittent, and tends to worsen at night and ease with movement. After some time, it becomes constant and may worsen with activity.
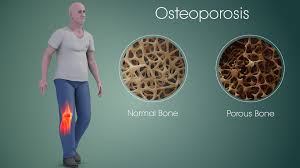
Bones debilitated by metastatic cancer can break or fracture. The fracture could occur with a fall or injury, although a weak bone can also fracture during daily activities. These fractures often cause severe and sudden pain. Pain can limit your mobility.
Fractures most often occur in the long bones of the arms and legs, as well as in the bones of the spine. Often, sudden pain in the middle of the back, for example, is a common symptom that a bone in the spine is fracturing and collapsing due to cancer.
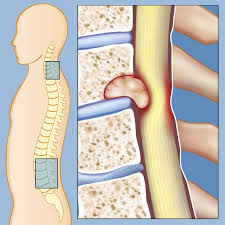
Cancer growth in the bones of the spine can make a pressure on the spinal cord. This is known as spinal cord compression and is a very severe condition. The spinal cord has nerves that enable you to move.
One of the most immediate manifestations of spinal cord compression is pain in the back or neck. Pressure on the spinal cord is capable of harming the nerves in it, causing symptoms like numbness and weakness in the area of the body below the tumor.
If a spinal cord compression isn’t treated at the right moment, the patient could become paralyzed. This condition affects the legs (so that the person is not able to walk) but if the tumor is pressing on the spinal cord in the neck, either the arms or the legs can result affected.
Occasionally, the first indicator that you may have of spinal cord pressure is trouble urinating because nerves from the spinal cord are in charge of the bladder. The patient can also feel more constipated (inasmuch as nerves from the spine help you move your bowels).
High blood calcium levels
When cancer disseminates to the bones, calcium from the bones could be released into the bloodstream. This causes high levels of calcium in the blood known as hypercalcemia. This can originate conditions such as constipation, nausea, loss of appetite, and extreme thirst. The high levels of calcium also lead you to make more urine, causing dehydration. It can also make you feel exhausted, weak, sleepy or even confused.