The majority of spinal cord injuries are the consequence of car accidents, falls, assaults and sports injuries.
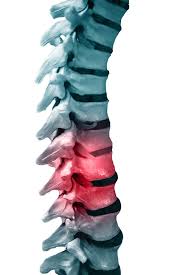
Patients who have a spinal cord injury ought not to be mobilized, except by emergency staff. The initial objectives are to ensure that people can breathe and avoid further damage. Therefore, the emergency staff is very careful when immobilizing the neck when treating a patient with a possible spinal cord injury. Generally, the patient is strapped on a rigid board and delicately padded to avoid movement. A stiff collar is used to prevent any movement of the neck. When the spine is seriously damaged, the vertebrae are not held in place or are broken, which makes the spine unstable. Therefore, even a slight movement causes a displacement of the spine and compresses the spinal cord. The compression of the cord increases the risk of permanent paralysis.
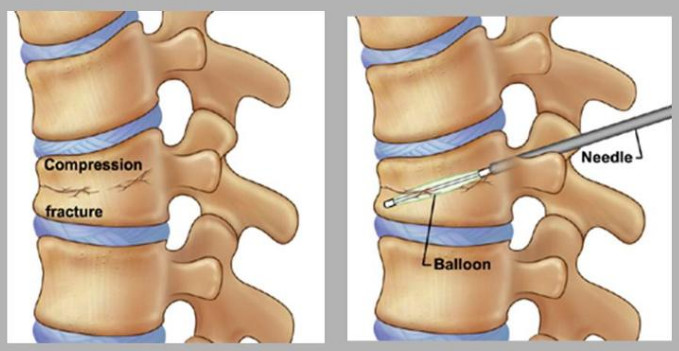
Surgery is necessary to remove blood and bone fragments if they have piled up and press on the spinal cord. If the spine is unsteady, the patient should be immobilized until the bone and other tissues have healed. In some cases, the surgeon inserts steel rods to stabilize the spine and prevent its movement which can originate additional injuries. If an injury causes a partial loss of function, doctors perform a surgical intervention soon after the injury, which allows a greater functional recovery. Nevertheless, the best time to perform surgery is disputed. Spinal cord surgery is carried out by neurosurgeons or orthopedic surgeons.
Pharmacological treatment is beneficial. These are the used drugs:
-Corticosteroids:There is no longer evidence to support the use of corticosteroids in spinal trauma
-Analgesics: If the injury causes pain, analgesics are administered. Opiates are often used during the first hours and days. Milder painkillers, such as paracetamol, acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be given later.
-Muscle relaxants: if spastic paralysis occurs, muscle relaxants such as baclofen or tizanidine are used.
All serious spinal injuries should be investigated carefully with a good clinical examination and appropriate imaging such as XRAYS, CT scan, MRI scans or advanced posture assessment using the EOS scanner.
The London Spine Unit specialises in the assessment and treatment of spinal injuries.