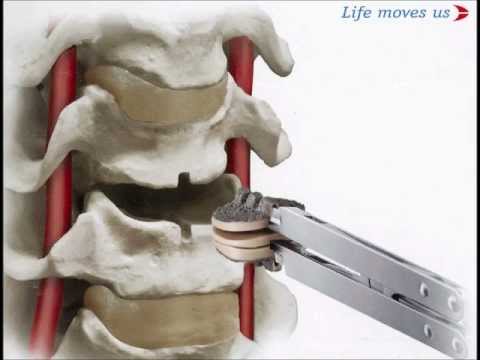
The cervical disc is the elastic pad that separates the vertebrae from each other, allowing them a small amount of movement in six axes. The sum of all these movements between the 7 cervical vertebrae results in the flexibility of the neck.
Cervical disc arthroplasty consists of the replacement of the intervertebral disc with a mobile prosthesis that completely restores the original mobility.
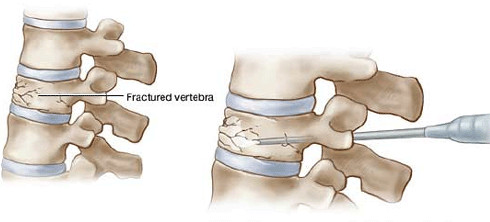
This technique is reserved for cases of disc failure (hernias or discopathies), although it is not convenient to practice them in all patients, since there are a number of criteria that exclude this possibility such as, for example, the existence of osteoarthritis or deformity. In general, this technique is reserved for young patients with little deterioration of the bony structures of the neck.
Benefits of the intervention
The aim of arthroplasty is to decompress the neural structures of the canal compressed by a herniated disc, restoring later the mobility of the cervical segment instead of fixing it with plates and screws.
The result regarding the compression symptoms is the same than the classic fixation technique, however, the mobility of the neck is not altered.
- Disc replacement improves function after surgery. Because the disc replacement devices preserves more normal neck motion, patients are able to reclaim a wider range of head and neck movement after surgery. Increased movement means increased day-to-day function and better quality of life.
- Motion preservation reduces stress on the spine. Traditional fusion surgery locks the treated vertebrae in place. The loss of motion can put stress on adjacent vertebrae and cause further degeneration in the future. Because disc replacement surgery maintains motion and prevents increased stress, it may help protect the adjacent vertebrae from additional degeneration over time.
- Minimally invasive surgery offers a faster recovery. After fusion surgery, patients must be immobilized for a period of time while the fused vertebrae heal. Recovery from disc replacement surgery is much faster; patients have returned to work within four days of surgery. Disc replacement surgery also means that patients don’t have to worry about some of the potential complications of fusion surgery.
Postoperative care
-The patient must change position in bed with help, avoiding to remain constantly face up.
-The drains (if any) will be removed 24 hours after surgery.
- Usually, the patient should get up the day after the intervention.
-Do not need a cervical collar, since the mobility of the neck must be respected. You should avoid sudden movements (sports) for 6 weeks.
-It will be prescribed postoperative medication, including an anti-inflammatory medication that you should take for 3 weeks even if there is no pain, since it prevents the formation of calcifications that block the mobility of the prosthesis.
-After discharge, you should contact the London Spine Unit if you have weakness in your limbs, fever and chills or suppuration from the wound.
-After discharge, likewise, you should avoid a series of movements and postures for 2 weeks: lifting weight, housework and driving.