Although PLDD is a minimally invasive treatment, it is not exempt from complications that, although, for the general term, are usually of a mild character, in some cases they can become more serious or complicated.
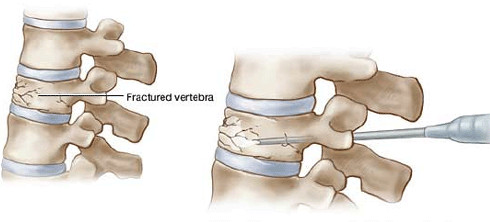
The objective of PLDD is to reduce the volume of the nucleus pulposus without affecting the fibrous ring or adjacent tissues. Therefore, it must be avoided that the heat generated by the laser has a high penetration power and thus reduce the probability of damage.
Among the most frequent complications are discitis, which is an inflammatory process that affects the intervertebral disc and the surface of the vertebral bodies.
It is suggested that the use of antibiotics could reduce the risk of infection of septic discitis, although its use is questioned. It can also be observed after the intervention the possibility of bleeding, along with the development of bruises, reflex sympathetic dystrophy, paraspinal muscle spasms, sacroiliac inflammation, new-onset root deficit, nerve root and sigmoid artery damage.
In the cervical and thoracic regions it should be taken into account that due to the anatomical location, with many vital structures, the intervention could carry a risk of emergence of retropharyngeal abscess, or pneumothorax, among other complications.
To avoid unwanted complications or adverse effects, emphasis is placed on that the procedure by means of PLDD must be performed by expert surgeons, with experience and trained in this procedure, being essential to monitor the patient and be alert to any complaint or pain during the intervention, making the necessary adjustments of power, frequency of pulses and intervals when applying the laser when it occurs an episode of pain or "burning" by the patient.